A large Earth-like granitic system exists on the Moon
By Newswise
Granites, which result from magma due to igneous activity, are nearly absent in our Solar System outside of Earth.
Yet over the past decade evidence by way of remote sensing systems used by geoscientists including Timothy Glotch, Ph.D., of Stony Brook University, have proven that notable silicic features like granites within a volcanic complex are on the Moon. Now additional research shows a likely large Earth-like granite system is present on the Moon. The finding, details of which are published in a Nature paper, may help expand knowledge of geothermal lunar processes.
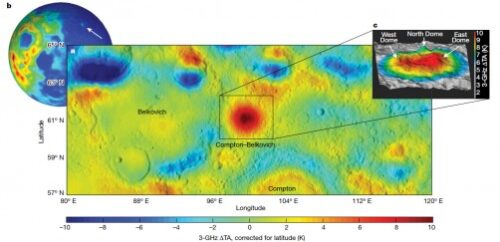
Previously, only a sampling of grains of granite was detected in the hundreds of kilograms of rocks returned by Apollo astronauts, and remote sensing studies since have found only a few small granite or granite-like features on the Moon. This research team used remote sensing measurements, specifically orbital microwave radiometry, and gravity measurements, to detect a large (greater than 50 kilometers in diameter) granitic body underneath the Compton-Belkovich Volcanic Complex (CBVC) on the Moon’s far side.
“Typically, granites require either plate tectonics or water-bearing magmas to form,” explains Glotch, co-author and Professor in the Department of Geosciences at Stony Brook University. “While the lunar interior contains small amounts of water, the Moon has never undergone plate tectonics. Therefore, this discovery of the granitic complex, or batholith underneath the CBVC, points to some not-yet-understood process that is responsible for the granitic formation.”
While Glotch and co-authors are not yet sure what the process is, there could be a number of possibilities. These could include a fractionation of KREEP (potassium-rare-earth-elements-and-phosphorus) basaltic liquids, or partial melting KREE-rich crust. If either of these were the case, it would require an abnormally hydrous mantle underneath the CBVC and a compositionally heterogenous lunar mantle.
The authors theorize that “the surprising magnitude and geographic extent of this feature imply an Earth-like, evolved granite system larger than believed possible on the Moon, especially outside of the Procellarum region…a phenomenon previously documented only on Earth.”
In addition to the discovery, the authors say of the remote sensing method that “this work illustrates a new tool for mapping planetary geothermal gradient from orbit through passive microwave radiometry, which can provide a window into crustal and interior heat-producing structures.”
Furthermore, they say that the methods used are generalizable, and “similar uses of passive radiometric data could vastly expand our knowledge of geothermal processes on the Moon and other planetary bodies.”
Glotch worked with the lead author, Matthew Siegler, of the Planetary Science Institute in Tucson, AZ, to conceptualize the study. The research is built out of more than 10 years of work by Glotch and other collaborators nationally to use remote sensing measurements of the Moon to map the presence and quality properties of anomalously silicic features on the lunar surface and interior.
The researchers previously identified a number of volcanoes, including CBVC and the Gruithuisen domes, as having granite-like compositions. These regions will be the target of a NASA rover mission in 2026.






